Relaying a Message From a Receptor Protein to a Molecule
Receptor Activated relay molecule Inactive protein kinase 1 Active protein kinase 1 Inactive protein kinase 2 ATP ADP Active protein kinase 2 P P PP Inactive protein kinase 3 ATP ADP Active protein kinase 3 P P PP i ATP. Up to 25 cash back Relaying a message from a membrane receptor to a molecule that performs a specific function within a cell is called - Answered by a verified Tutor.

Solved Relaying A Message From A Membrane Receptor To A Chegg Com
Relaying a message from a membrane receptor to a molecule.
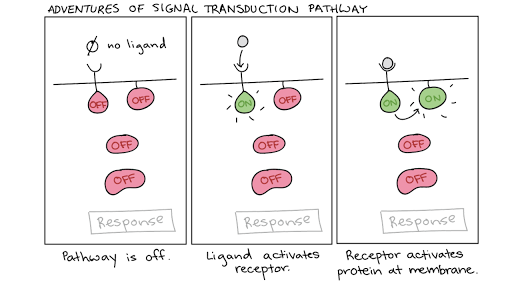
. A process in which surface proteins are receptors. A couple of cytoplasmic pro teins relay the message. Relaying a message by phosphorylating downstream proteins.
Transport a signal through the lipid bilayer. Question 9 of 20 50 50 Points Relaying a message from a receptor protein to a molecule that performs a specific function within a cell is called. Structurally the signaling molecules used by.
Its signal transduction Im sure of it. Relay message from the inside of the mebrane throughout the cytoplasm. Glycoproteins are recognized by other cells.
In plant cells _____ may contain organic nutrients pigments and poisons. Relaying a message from a membrane receptor to a molecule that performs a specific function within a cell occurs when A a signaling molecule binds to a protein that extends to the outside of the cell B a protein receptor on the interior of the membrane become bounds by a signaling molecule C the extracellular matrix is moved to the inside of. B selective permeability.
As the concentration of hormone increases the concentration of. Relaying a message from a membrane receptor to a molecule that performs a specific function within a cell occurs when Relaying a message from a membrane receptor to a molecule that performs a specific function within a cell occurs when the extracellular matrix is moved to the inside of the cell. Relay proteins Activated tyrosine kinase regions Fully activated receptor tyrosine kinase.
C signal transduction. 9 Relaying a message from a membrane receptor to a molecule that performs a specific function within a cell is called. Ligands bond to receptor proteins and cause the protein to relay a message to intracellular proteins.
Relay proteins simply pass the message to the next signaling component in the chain. Relaying a message from a receptor protein to a molecule that performs a specific function within a cell is called. A receptor in the cells membrane binds the signal molecule.
A inhibition. C signal transduction. A cell sends a signal molecule.
D competition. Place the following events of signal transduction in order activated protein travels inside the nucleus a new protein is made. Presumably because the nuclear hormone receptor protein binds a single molecule of hormone and each specific DNA recognition sequence in a steroid-hormone-responsive gene acts independently.
How Genes Are Controlled 4. These acetylcholine receptors are composed of five protein chains arranged in a long tube that crosses the cell membrane. Diverse proteins embedded in a phospholipid bilayer.
Relaying a signal from the outside to the inside of the plasma membrane. Many different kinds of molecules transmit information between the cells of multicellular organisms. Osmosis can be defined as.
Although all these molecules act as ligands that bind to receptors expressed by their target cells there is considerable variation in the structure and function of the different types of molecules that serve as signal transmitters. When a signaling molecule binds to a G-protein-coupled receptor in the plasma membrane a GDP molecule associated with the α subunit is exchanged for GTP. The β and γ subunits dissociate from the α subunit and a cellular response is triggered either by.
G proteins a relay a message from an activated receptor to an enzyme that activates a second messenger b are GTP molecules c terminate cell signaling d directly activate protein kinases e function as first messengers. Relaying a message from the cytosolic side of the membrane throughout the cytoplasm. A protein receptor on the interior of the membrane become bounds by a signaling molecule.
Dampening the message once the signal molecule has left the receptor. Central nervous system relaying messages from nerve to nerve for more information on acetylcholine receptors from a genomics perspective visit the Protein of the Month at the European Bioinformatics Institute. Relaying a message from a membrane receptor to a molecule that performs a specific function within a cell occurs when.
A gene is turned on. Relaying a message from a receptor protein to a molecule that performs a specific function within a cell is called. A G protein is an example of a secondary messenger molecule that is involved in signal transduction for protein derived of hormones which interact with surface receptors and require secondary messenger molecules to take their message to the nucleus to enact a response.
Relay a signal from the outside to the inside of the cell. A protein that can bind to a small molecule to receive a message from other cells signal transduction the process of receiving and relaying information in a message across a membrane andor different parts of a cell.

Apbio Chapter 5 6 Cell Signaling Flashcards Quizlet

Signal Transduction Pathway Cell Signaling Article Khan Academy
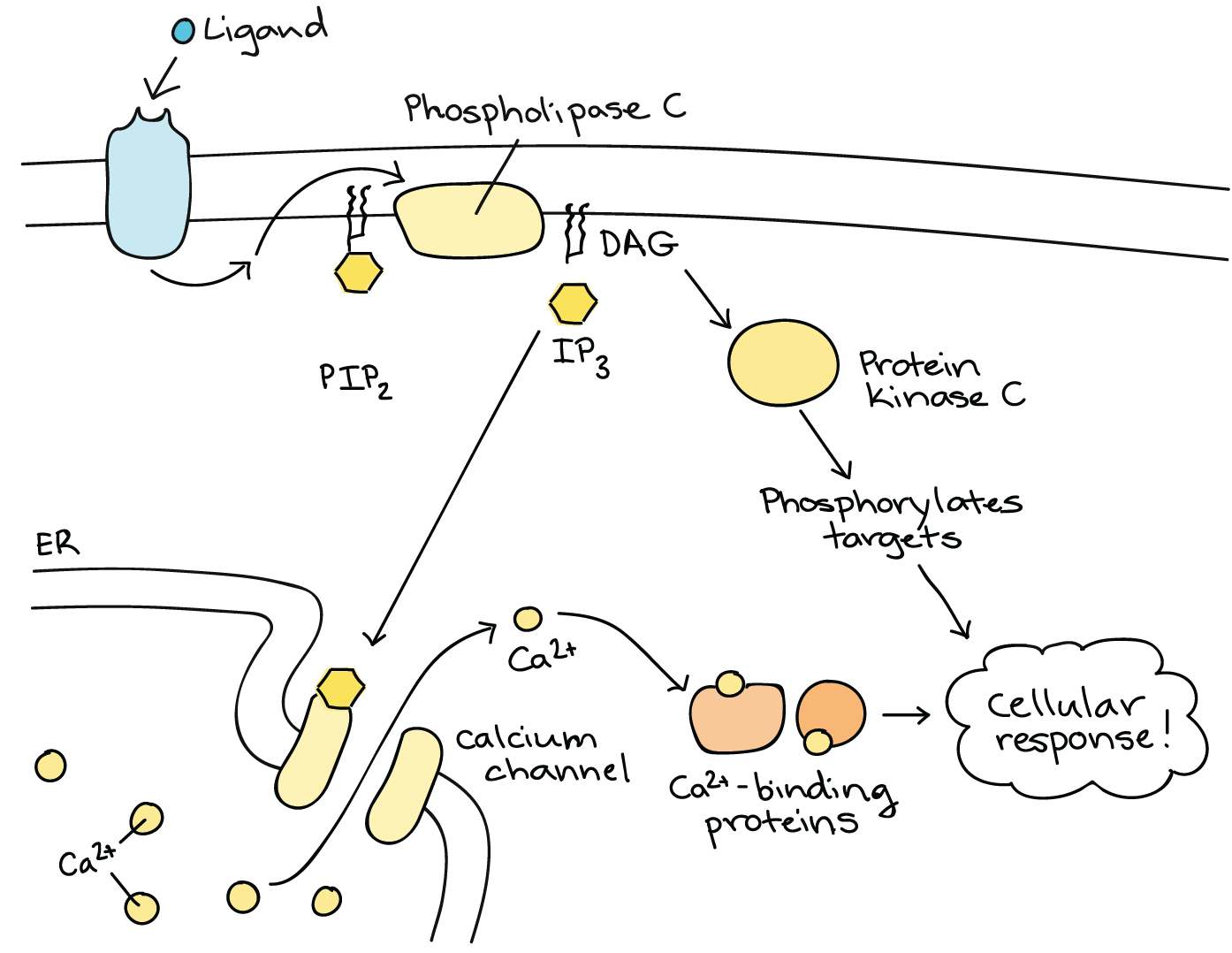
Signal Transduction Pathway Cell Signaling Article Khan Academy
No comments for "Relaying a Message From a Receptor Protein to a Molecule"
Post a Comment